Pool of Stake: From Proof of Work to Proof of Stake

One of the most popular vectors of block projects has recently been the solution of the problems of traditional mining. But, as it turned out, even these solutions have their flaws.
Today, let's talk about one of the most promising projects of this year, which, perhaps, will radically change the principles that existed in the crypto-currency market before that time. In order not to be unfounded: ICO within the framework of the project Pool of Stake started quite recently, on July 20, and already at the time of writing the review (July 31) its founders managed to collect € 2.58 million, overcoming the soft cap threshold of € 2 million.

Proof of Work History
With the advent of bitcoin in 2009 as the first of its kind crypto currency, blocking technology as its basis and mining as an opportunity to earn coins, more and more people were able to earn effectively using the Proof of Work algorithm. Initially, any miner had enough PC and installed application, because mining did not require as much processing power as it does now.
The bitcoin network and the number of participants in it grew progressively, and with them the need for more powerful equipment. So users began to use special equipment specifically designed for mining. With its appearance, people began to collect the first mining farms, after which the use of the Proof of Work algorithm developed into the emergence of large mining pools, which resulted in a number of negative consequences.
Since the emergence of expensive specialized equipment for mining, fewer miners have been able to mine the crypto currency. We are talking about small miners, who were replaced by professional pools, entire organizations that earn on the extraction of coins. From that moment, the very concept of decentralization, which Satoshi Nakamoto laid in bitcoin and described in the well-known White Paper bitcoin, began to lose its meaning, and mining became more centralized.
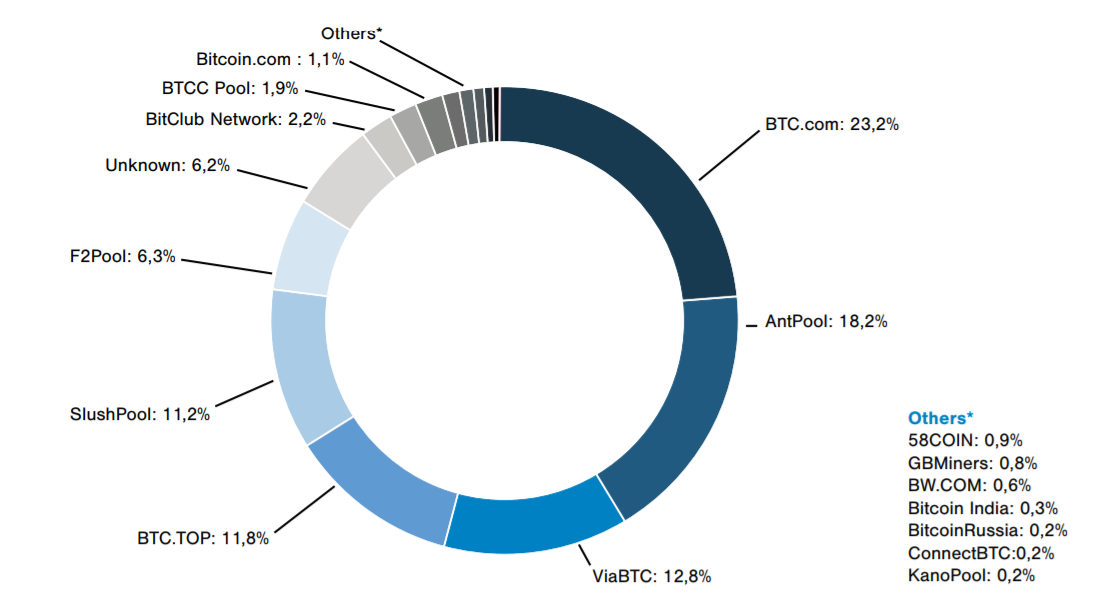
The situation that we have today is as follows. Smaller miners do not have the slightest opportunity to earn a crypto currency, the hashtra is controlled by large mining pools, which, in turn, calls into question the existence of the concept of decentralization in PoW, the maximum transaction speed with the current block size is 7 transactions per second, the transaction value reaches $ 50, and the annual transaction The consumption of electricity due to mining can easily compete with many countries.
In their technical documentation, the developers of the Pool of Stake project provided a diagram of the bitcoine hash and mining pools that control it. The situation is that as of January 2018, 77.1% of the total hashed control the 5 largest pools, among them: BTC.com (23.2%), AntPool (18.2%), ViaBTC (12.8%), BTC.TOP (11.8%) and SlushPool (11.2%). This proves once again that the principles of the Proof of Work protocol do not allow to properly observe the concept of decentralization, and "power" is concentrated in the hands of centralized structures.

The appearance of Proof of Stake
Low efficiency and high power consumption using the Proof of Work algorithm became the reason for creating in 2012 a completely new mechanism - Proof of Stake, which is radically different from its predecessor. Instead of the usual mining, PoS uses a new concept - "staking" (staking). Miners, as such, are absent, as is the need for expensive equipment. Instead of them new participants appeared - steakers.
Proof of Stake has become a more effective alternative to Proof of Work. Steykers do not create new coins, but only confirm transactions, receiving a reward for this in the form of part of the transaction commissions. In this case, the validator that confirms the transaction is determined based on the number of coins in its account. Thus, the more coins, the more chances to get a reward in the form of commission for the transaction.
Initially, the mission of Proof of Stake was to create a more efficient, environmentally friendly and truly decentralized algorithm that would become a worthwhile alternative to Proof of Work. Nevertheless, not everything turned out as smoothly as it was supposed, therefore, Proof of Stake has its own significant drawbacks.

Disadvantages of Proof of Stake
The first and one of the main problems of the PoS algorithm is the high risk of monopolization. The concept of the mechanism assumes the possibility to be chosen to confirm the transaction and to receive the corresponding reward depends on the number of coins in the user's wallet. On the one hand, it is more effective than in Proof of Work, but on the other hand, not everyone can afford to meet the requirement "the more the better."
While participants with large reserves of crypto currency in their wallets will receive most of all coins received, smaller participants will remain in much less favorable terms. In fact, their chances of receiving rewards are minimized, even given that the concept of decentralization is being respected. Hence one more negative consequence - the so-called "51% attack", in which steakers with more than 51% of the total volume of tokens become a threat to the rest of the participants.
The second problem of Proof of Stake is also associated with small miners. The mechanism provides for a round-the-clock connection in order to be able to confirm the transaction, but not all miners, even large ones, are ready for this. The result - decentralization, which we wanted to achieve with the help of Proof of Stake, is only achieved conditionally.
Pool of Stake
"The future of blockade for Proof of Stake". In order for the mechanism to really justify itself, it needs effective changes and solutions that will allow absolutely all participants without exception to enjoy its advantages. One of these solutions will be Pool of Stake, which is currently being developed in the framework of the same-named block-project.
The creators of Pool of Stake offer small participants in the system to get rid of the existing shortcomings of the algorithm and unite in one pool of steakers, in parallel with this, combining their coins. Thus, they will be able to take part in stealing along with large stakes, round-the-clock confirming transactions and getting much more profit from transaction commissions than working alone.
How do users participate in the pool pool of Stake? Why does the platform release two different tokens at the same time? How does the steak take place and how are the rewards allocated? What are the prospects for such a blocking project? Get answers to all these questions in the next part of the Pool of Stake project overview.
FOR MORE INFORMATION :
Website: https://www.poolofstake.io
Whitepaper: https://www.poolofstake.io/wp-content/uploads/2017/12/PoolofStake-whitepaper_ENG_V11.pdf
Bitcointalk ANN: https://bitcointalk.org/index.php?topic=3283742.0
Telegram: https://telegram.me/poolofstake
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/poolofstake
Youtube: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCenEbx5MwCF7kjTAWU-jv_g?
Medium: https://medium.com/@poolofstake
Twitter: https://twitter.com/poolofstake
LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/company/pool-of-stake
Github: https://github.com/poolofstake/PSK
Whitepaper: https://www.poolofstake.io/wp-content/uploads/2017/12/PoolofStake-whitepaper_ENG_V11.pdf
Bitcointalk ANN: https://bitcointalk.org/index.php?topic=3283742.0
Telegram: https://telegram.me/poolofstake
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/poolofstake
Youtube: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCenEbx5MwCF7kjTAWU-jv_g?
Medium: https://medium.com/@poolofstake
Twitter: https://twitter.com/poolofstake
LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/company/pool-of-stake
Github: https://github.com/poolofstake/PSK
ETH : 0x37B6953a3D9c40D5e40Dfc7DA2B8A58223b2a583
Komentar
Posting Komentar